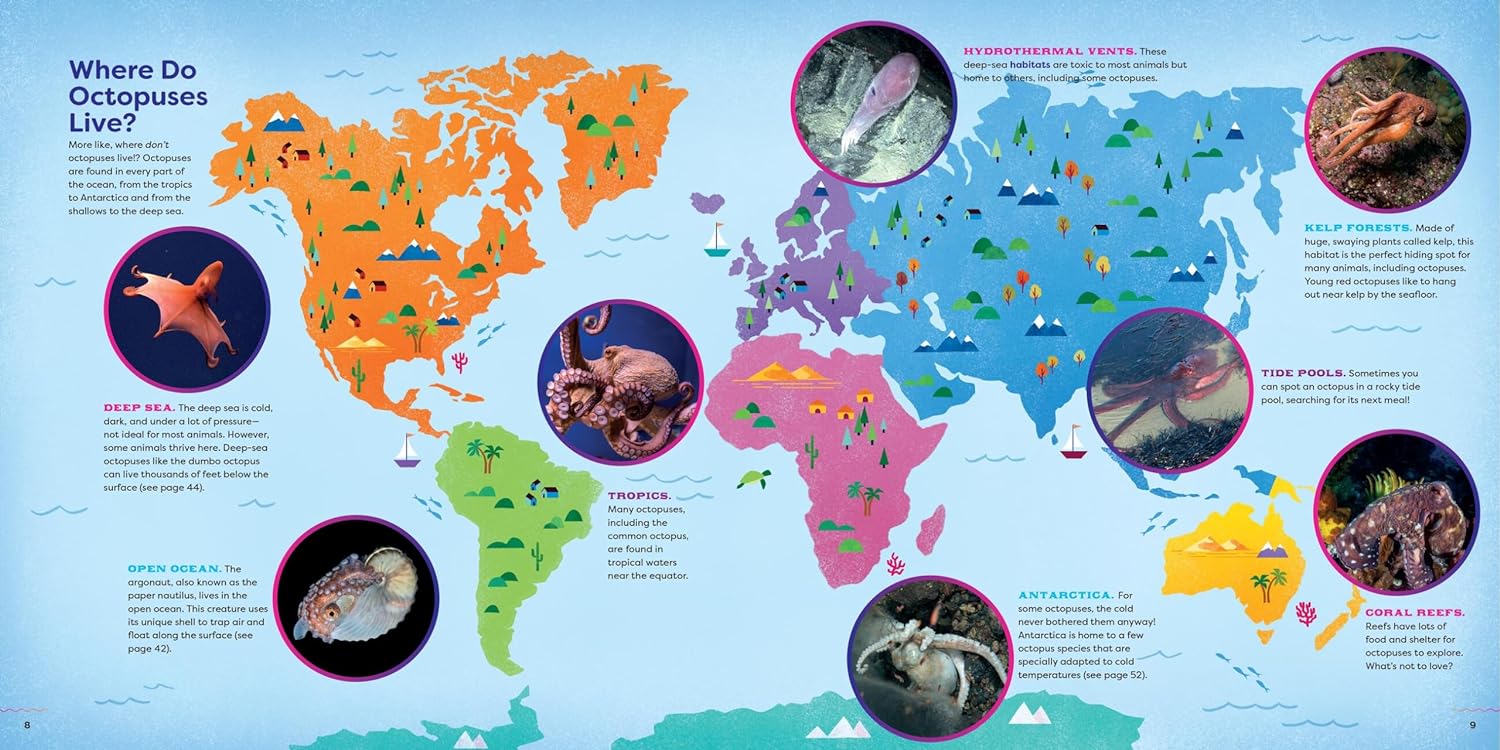
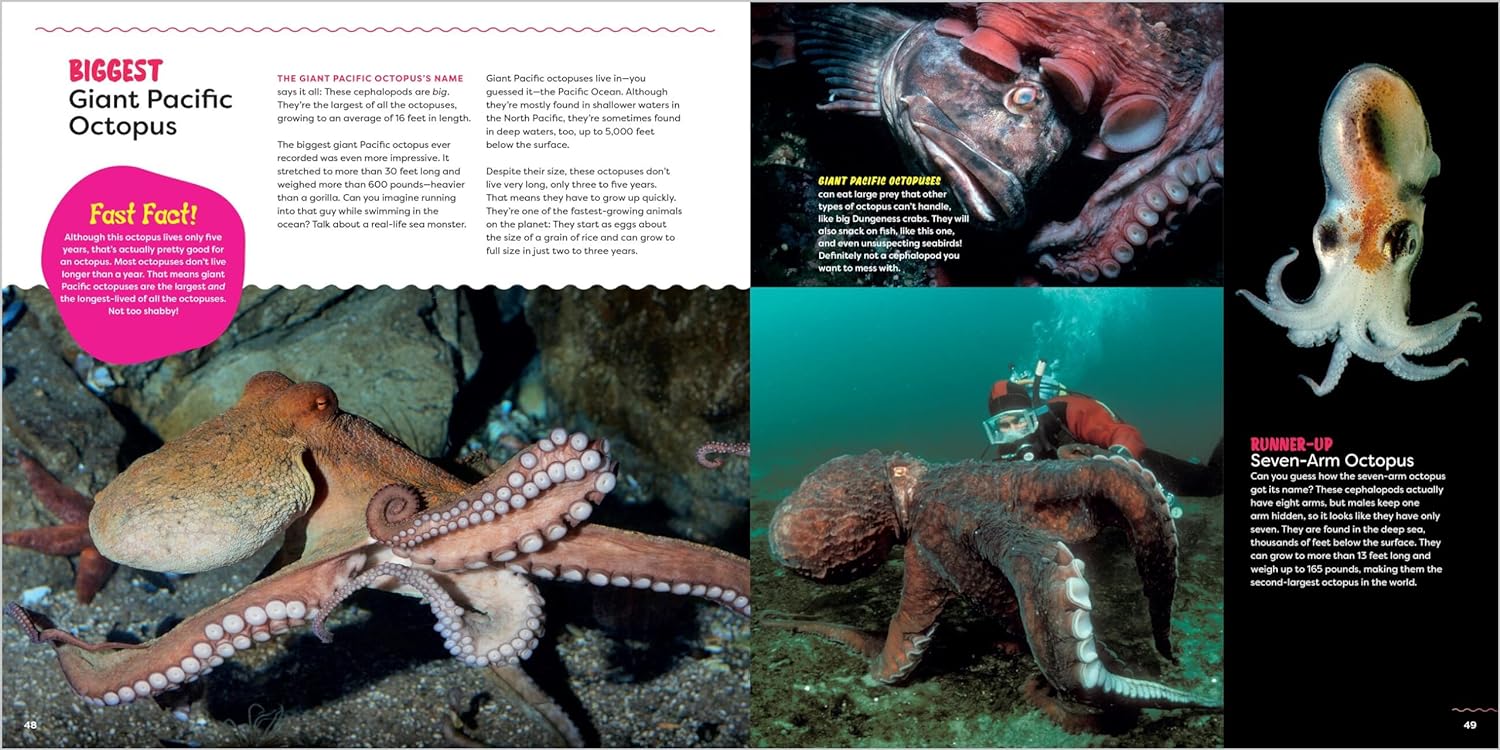
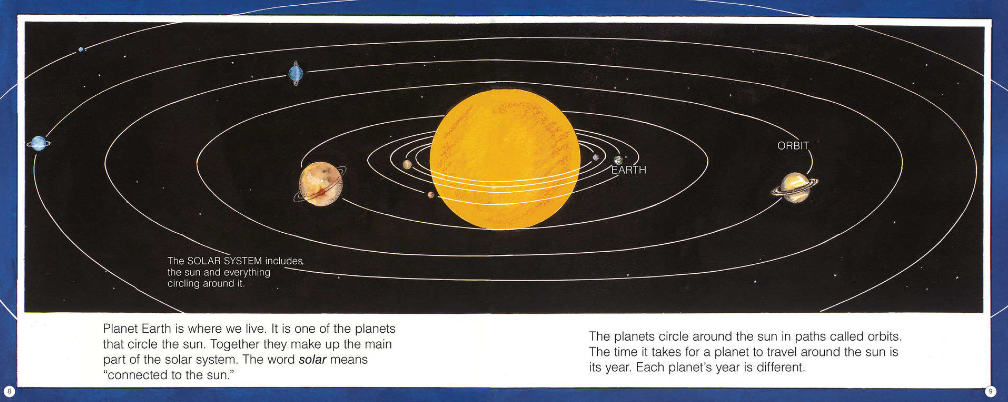
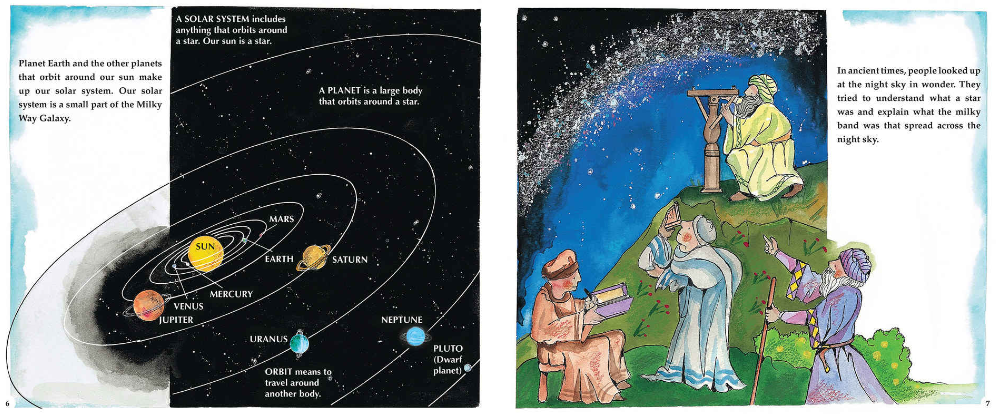
The Uninhabitable Earth (Adapted for Young Readers): Life After Warming
Author: David Wallace-Wells
Published October 10th, 2023 by Delacorte Press
Summary: An exploration of the devastating effects of global warming—current and future—adapted for young adults from the #1 New York Times bestseller. This is not only an assessment on how the future will look to those living through it, but also a dire overview and an impassioned and hopeful call to action to change the trajectory while there is still time.
The climate crisis that our nation currently faces, from rising temperatures, unfathomable drought, devastating floods, unprecedented fires, just to name a few, are alarming precursors to what awaits us if we continue on our current path. In this adaptation for young adults from the #1 New York Times bestseller, journalist David Wallace-Wells tells it like it is, and it is much worse than anyone might think. Global warming is effecting the world, if left unchecked, it promises to transform global politics, the meaning of technology and the trajectory of human progress.
In sobering detail, Wallace-Wells lays out the mistakes and inaction of past and current generations that we see negatively affecting all lives today and more importantly how they will inevitably affect the future. But readers will also hear—loud and clear—his impassioned call to action, as he appeals to current and future generations, especially young people. As he “the solutions, when we dare to imagine them . . . are indeed motivating, if there is to be any chance of preserving even the hope for a happier future—relatively livable, relatively fulfilling, relatively prosperous, and perhaps more than only relatively just.”
About the Author: David Wallace-Wells is a columnist and deputy editor at New York magazine. He has been a national fellow at the New America Foundation and was previously the deputy editor of The Paris Review. He lives in New York City.
Review: This is an intense book. Like shared in the excerpt below, climate change is a “hyperobject” which makes it seems so intimidating, but David Wallace-Wells does a good job of taking this daunting reality and potential future and breaking it down for the reader though he definitely did not sugar coat anything for the Young Reader edition. It is terrifying and a call to action. But it is also so important, and I am so glad that the author and publisher decided to make it available and accessible for young readers.
I really liked the structure of the books. Wallace-Wells didn’t combine everything and just throw it all at the reader. Each of the four parts are broken up into smaller topics where he focuses on just those aspects. For example, climate changes’ effect on hunger, wild fires, air, plagues, etc. This allows the reader to process each part and not get too overwhelmed.
I also appreciate that he added an afterword which has updates since the original book was published. I think this shows readers that science changes and needs to be updated and make the book more reliable.
I do need to add a warning: The book will not help with eco-anxiety. If anything, it will make it worse. I had to pause the book sometimes to take a breath.
Tools for Navigation: This text could definitely be used in a high school course looking at global warming and climate change since he does a great job of connecting the science to reality. I would love to see this text used in English class as the science is studied in science: a cross-curricular gem of an opportunity.
Most importantly, though, this book needs to get into kids’ hands. It reminds them of the importance of the decisions that our current and future generations need to make about our environment.
Discussion Questions:
- What are some actions that we could begin doing to help with the future?
- Why did the author add to the book when he rewrote it for Young Readers?
- How has human progression been the downfall for our Earth?
- Why does climate change seem so daunting to many and thus leads to doing nothing?
- What do you think is the most important thing that humans need to do now?
- How will climate change directly impact where you live?
Flagged Passages: Chapter 1: Cascades
The world will be what we make it–perhaps what you make it. The timelines are indeed that short.
Consider the speed of change. The earth has experienced five mass extinctions before the one we are living through now, each so complete a wiping of the fossil record that it functioned as an evolutionary reset, the planet’s phylogenetic tree first expanding, then collapsing, at intervals, like a lung: 86 percent of all species dead 450 million years ago; 70 million years later, 75 percent; 125 million years later, 96 percent; 50 million years later, 80 percent; 135 million years after that, 75 percent again. All but one of these involved climate change produced by greenhouse gas. The most notorious was 250 million years ago; it began when carbon dioxide warmed the planet by five degrees Celsius, accelerated when that warming triggered the release of methane, another greenhouse gas, and ended with all but a sliver of life on Earth dead. We are currently adding carbon to the atmosphere at a considerably faster rate–by most estimates, at least ten times faster. The rate is one hundred times faster than at any point in human history before the beginning of industrialization. And there is already, right now, fully a third more carbon in the atmosphere than at any point in the last 800,000 years–perhaps in as long as 15 million years. There were no humans then. The oceans were more than a hundred feet higher.
Many perceive global warming as a sort of moral and economic debt, accumulated since the beginning of the Industrial Revolution and now come due after several centuries. In fact, more than half the carbon exhaled into the atmosphere by the burning of fossil fuels has been emitted in just the past three decades. The United Nations established its climate change framework in 1992, building a political consensus out of a scientific consensus and advertising it unmistakably to the world; this means we have now done as much damage to the environment knowingly as we ever managed in ignorance. Global warming may seem like a distended morality tale playing out over several centuries and inflicting a kind of Old Testament retribution on the great-great-grandchildren of those responsible, since it was carbon burning in eighteenth-century England that lit the fuse of everything that has followed. But that is a fable about historical villainy that acquits those of us alive today–unfairly. The majority of the burning has come since the 1994 premiere of Friends. A quarter of the damage has been done since Barack Obama was elected president, and Joe Biden vice president, in 2008. Since the end of World War II, the figure is about 90 percent. The story of the industrial world’s kamikaze mission is the story of a single lifetime–the planet brought from seeming stability to the brink of catastrophe in the years between a baptism or bar mitzvah and a funeral.
It is the lifetime of many of the scientists who first raised public alarm about climate change, some of whom, incredibly, remain working–that is how rapidly we have arrived at this promontory, staring down the likelihood of three degrees Celsius of warming by the year 2100. Four degrees is possible as well–perhaps more. According to some estimates, that would mean that whole regions of Africa and Australia and the United States, parts of South America north of Patagonia, and Asia south of Siberia would be rendered brutally uncomfortable by direct heat, desertification, and flooding. Certainly, it would make them inhospitable, and many more regions besides. Which means that, if the planet was brought to the brink of climate catastrophe within the lifetime of a single generation, the responsibility to avoid it belongs with a single generation, too. We all also know that second lifetime. It is ours.
I am not an environmentalist and don’t even think of myself as a nature person. I’ve lived my whole life in cities, enjoying gadgets built by industrial supply chains I hardly think twice about. I’ve never gone camping, not willingly anyway, and while I always thought it was basically a good idea to keep streams clean and air clear, I also always accepted the proposition that there was a trade-off between economic growth and its cost to nature–and figured, well, in most cases I’d probably go for growth. I’m not about to personally slaughter a cow to eat a hamburger, but I’m also not about to go vegan. In these ways–many of them at least–I am like every other American who has spent their life fatally complacent, and willfully deluded, about climate change, which is not just the biggest threat human life on the planet has ever faced but a threat of an entirely different category and scale. That is, the scale of human life itself.
A few years ago, I began collecting stories of climate change, many of them terrifying, gripping, uncanny narratives, with even the most small-scale sagas playing like fables: a group of Arctic scientists trapped when melting ice isolated their research center, on an island populated also by a group of polar bears; a Russian boy killed by anthrax released from a thawing reindeer carcass, which had been trapped in permafrost for many decades. My file of stories grew daily, but very few of the clips, even those drawn from new research published in the most pedigreed scientific journals, seemed to appear in the coverage about climate change the country watched on television and read in its newspapers. In those places, climate change was reported, of course, and even with some tinge of alarm. But the discussion of possible effects was misleadingly narrow, limited almost invariably to the matter of sea-level rise. Just as worrisome, the coverage was sanguine, all things considered. As recently as the 1997 signing of the landmark Kyoto Protocol, two degrees Celsius of global warming was considered the threshold of catastrophe: flooded cities, crippling droughts and heat waves, a planet battered daily by hurricanes and monsoons we used to call “natural disasters” but will soon normalize as simply “bad weather.” More recently, the foreign minister of the Marshall Islands offered another name for that level of warming: “genocide.”
This is not a book about the science of warming; it is about what warming means to the way we live on this planet. But what does that science say? It is complicated research, because it is built on two layers of uncertainty: what humans will do, mostly in emitting greenhouse gases, but also in how we adapt to the environment we have transformed and how the climate will respond, both through straightforward heating and a variety of more complicated and sometimes contradictory feedback loops. But even shaded by those uncertainty bars, it is also very clear research, in fact terrifyingly clear. The United Nations’ Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) offers the gold-standard assessments of the state of the planet and the likely trajectory for climate change. In its latest report, the IPCC suggested the world was on track for about 3 degrees of warming, bringing the unthinkable collapse of the planet’s ice sheets not just into the realm of the real but into the present.
Because these numbers are so small, we tend to trivialize the differences between them–one, two, four, five. Human experience and memory offer no good analogy for how we should think of those thresholds, but, as with world wars or recurrences of cancer, you don’t want to see even one.
At two degrees of warming, the ice sheets will likely begin their collapse, 400 million more people could suffer from water scarcity, and major cities in the equatorial band of the planet will become lethally hot in summer. There would be thirty-two times more extreme heat waves in India, and each would last five times as long, exposing ninety-three times more people. This is our best-case scenario.
At three degrees, southern Europe would be in permanent drought, and the average drought in Central America would last nineteen months longer and in the Caribbean twenty-one months longer. In northern Africa, the figure is sixty months longer–five years. The areas burned each year by wildfires would double in the Mediterranean and sextuple, or more, in the United States.
At four degrees, damages from river flooding could grow thirtyfold in Bangladesh, twentyfold in India, and as much as sixtyfold in the United Kingdom. In certain places, six climate-driven natural disasters could strike simultaneously. Conflict and warfare could double.
Even if we pull the planet up short of two degrees by 2100, we will be left with an atmosphere that contains 500 parts per million of carbon–perhaps more. The last time this was the case, sixteen million years ago, the planet was not two degrees warmer; it was somewhere between five and eight, giving the planet about 130 feet of sea-level rise, enough to draw a new American coastline as far west as I-95. Some of these processes take thousands of years to unfold, but they are also irreversible and therefore effectively permanent. You might hope to simply reverse climate change; you can’t. It will outrun all of us.
This is part of what makes climate change what the theorist Timothy Morton calls a “hyperobject”–a conceptual fact so large and complex that, like the internet, it can never be properly comprehended. There are many features of climate change–its size, its scope, its brutality–that alone satisfy this definition; together, they might elevate it into a higher and more incomprehensible conceptual category yet. But time is perhaps the most mind-bending feature, the worst outcomes arriving so long from now that we reflexively discount their reality.
Read This If You Love: Nonfiction, specifically about climate change
Recommended For:




**Thank you to Nicole Banholzer PR and the Publisher for providing a copy for review!**